It is a combination of various cell receptors in the cell membrane usually made up of sugars and proteins. They receive chemical messages from other cells called signaling moleculesWhen these molecules.
Ligands Receptors Article Khan Academy
These associated plasma membrane molecules can modulate virtually all integrin functions by altering signal transduction arising from integrin ligation.

. The external messenger signaling molecule may cause the protein to change shape and internal signal cascade. These proteins include cell-surface receptor proteins which bind the signal molecule plus a variety of intracellular signaling proteins that distribute the signal to appropriate parts of the cell. They typically interact with cell-surface receptors.
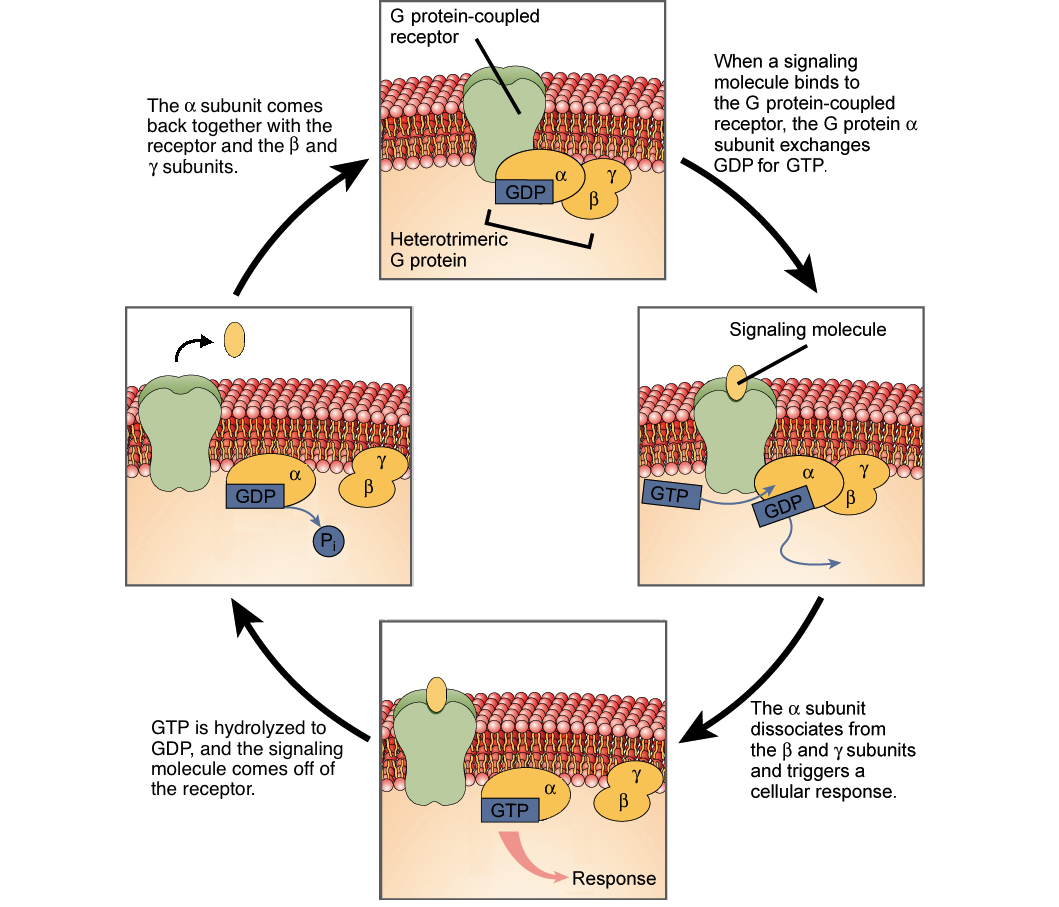
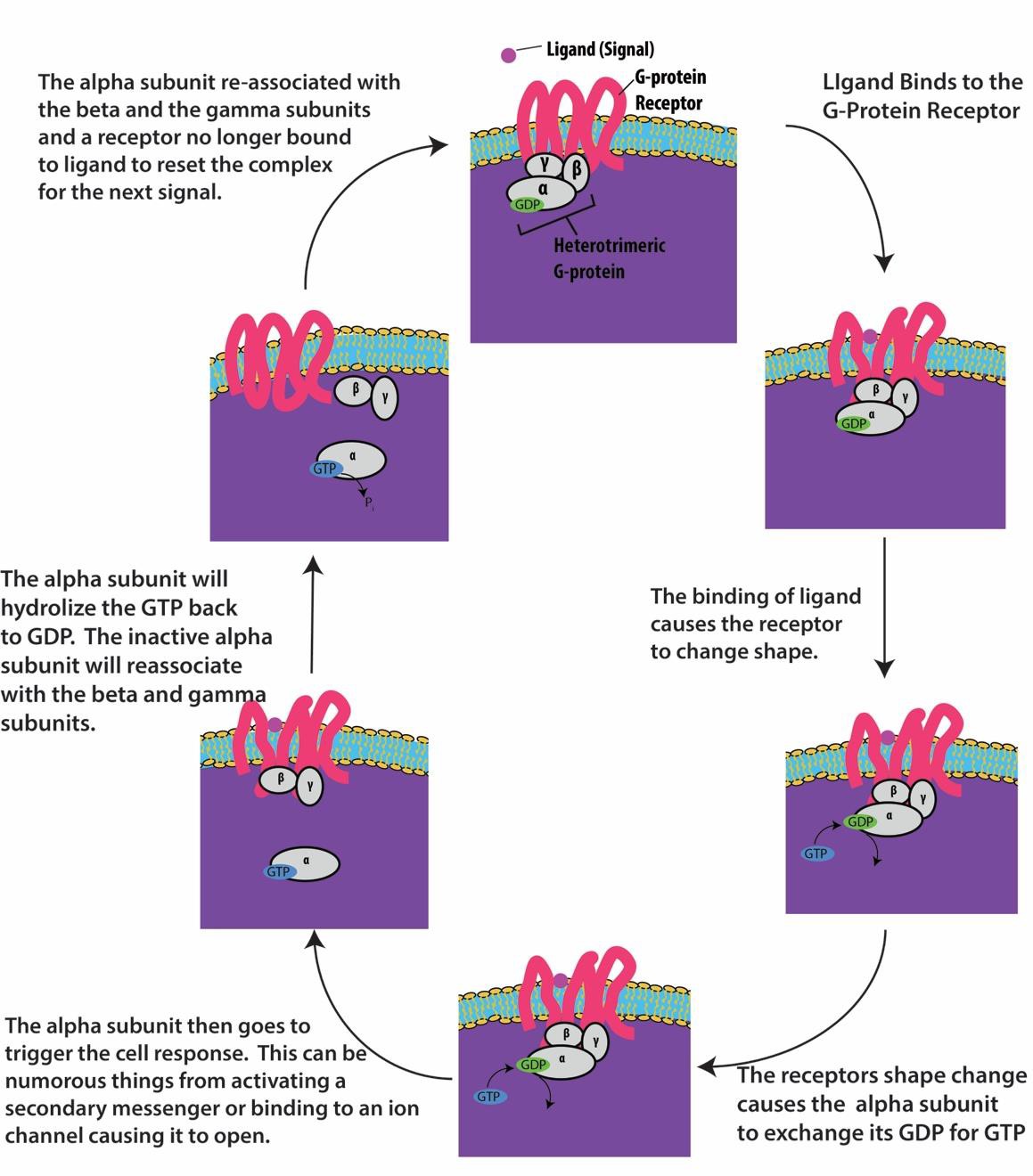
These receptors span the plasma membrane and perform signal transduction in which an extracellular signal is converted into an intercellular signal. In the past two years new examples of signaling through heterotrimeric G proteins. They thereby enable the protein they are part of to dock on the membrane and interact with other recruited signaling.
The signal transduction cascade begins when adenylyl cyclase a membrane- bound enzyme is activated by G-protein molecules associated with the adrenergic receptor. Many signal transduction pathways use second messengers to A transport a signal through the lipid bilayer portion of the plasma membrane B relay a signal from the outside to the inside of the cell C relay the message from the inside of the membrane throughout the cytoplasm Damplify the. Membrane proteins that bind to signals by which cells communicate are called _____.
Pleckstrin homology PH domains first described in the Pleckstrin protein in blood platelets bind to the charged headgroups of specific phosphorylated inositol phospholipids that are produced in the plasma membrane in response to an extracellular signal. Cell-surface receptors also known as transmembrane receptors are integral proteins that bind to external signaling molecules. These dynamics add spatial and temporal context to the more well-recognized information communication from the cell membrane to the nucleus following ligand binding to membrane receptors.
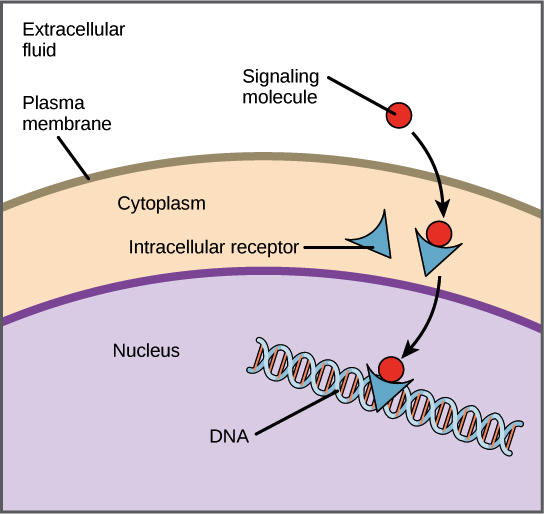
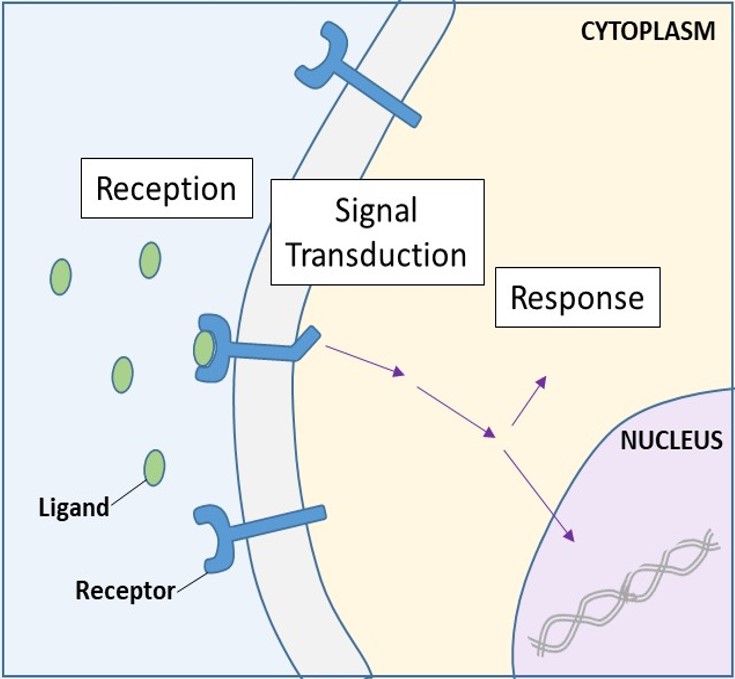
Among the intracellular signaling. A membrane protein receptor may have a binding site with a specific shape that fits the shape of a chemical messenger such as a hormone. Chapter 11 Cell Communication Receptors in the Plasma Membrane Most water-soluble signaling molecules generally too large to pass freely through the plasma membrane bind to specific sites on receptor proteins embedded in the plasma membrane of the cell.
Nitroglycerin and Viagra affect the NO pathway. There are a variety of other ligands such as nitric oxide NO gas. These membrane receptor proteins can transmit the information from the outer portion of the cell to the inner portion of the cell.
Many of the proteins in the cell membrane are involved in cellular communication. These receptors play a key role not only in cell identification through antigens the main basis for antibody production of the immune system but also as binding sites for chemical messengers like hormones. Cell-adhesion molecules Channel protein gates respond to all these stimuli except _____.
The specific ligand binds to the receptor on the plasma. Peptide protein hormones are an example. Water soluble hydrophilic ligands can not pass directly through the cell membrane.
This happens when the conformation of the cell changes after the binding of the specific ligand molecule. Here the signal is transmitted and amplified through transduction by the canonical molecular eg Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases MAPK pathways. A signal molecule that binds to a plasma-membrane protein is a.
Preview this quiz on Quizizz. They also depend on elaborate systems of proteins that each cell contains to enable it to respond to a particular subset of these signals in a cell-specific way. Most water-soluble signal molecules bind to specific sites on receptor proteins in the plasma membrane There are three main types of membrane receptors.
What membrane proteins bind to signals by which cells communicate. Glycoprotein-channels facilitate cell to cell recognition by specific binding between the receptors and ligands of the adjacent cells. The three major receptors are G-protein coupled receptors ion channel receptors and tyrosine kinase receptors.
This type of receptor spans the plasma membrane and performs signal transduction through which an extracellular signal is converted into an intracellular signal. Once a ligand binds to a receptor the signal is transmitted through the membrane. Changes in electrical potential voltage across the plasma membrane.
A signal molecule that binds to a plasma-membrane protein is a. In effect these binding sites allow a cell to receive. A cAMP phosphatase B G protein C phosphodiesterase D protein kinase E protein 3.
Earn 20 pts. A diverse group of plasma membrane proteins have been found associated with integrins in supramolecular complexes. Cell-surface receptors also known as transmembrane receptors are cell surface membrane-anchored integral proteins that bind to external ligand molecules.
_____ are membrane proteins that bind to signals by which cells communicate. G protein-coupled receptors Receptor tyrosine kinases Ion channel receptors Copyright 2008 Pearson Education Inc publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings. The membrane proteins join at different gap junctions or show inter-cellular joining which aids in cell-cell communication.
Do plant cells communicate using hormones.
Chapter 9 Cell Communication Introduction To Molecular And Cell Biology

Khan Academy Plasma Membrane Cell Membrane Signal Transduction
Ligands Receptors Article Khan Academy
Chapter 9 Cell Communication Introduction To Molecular And Cell Biology

Figure 15 3 The Binding Of Extracellular Signal Molecules To Either Cell Surface Receptors Or Intracellular Recept Molecules Plasma Membrane Molecular Biology

Xl 7c Midterm 1 Study Flashcards Quizlet

Figure 15 9 Various Responses Induced By The Neurotransmitter Acetylcholine Molecular Biology Of The Cell Ncbi B Molecular Biology Acetylcholine Molecular

Figure 15 8 An Animal Cell S Dependence On Multiple Extracellular Signals Molecular Biology Of The Cell Ncbi Bookshe Animal Cell Molecular Biology Biology

0 Comments